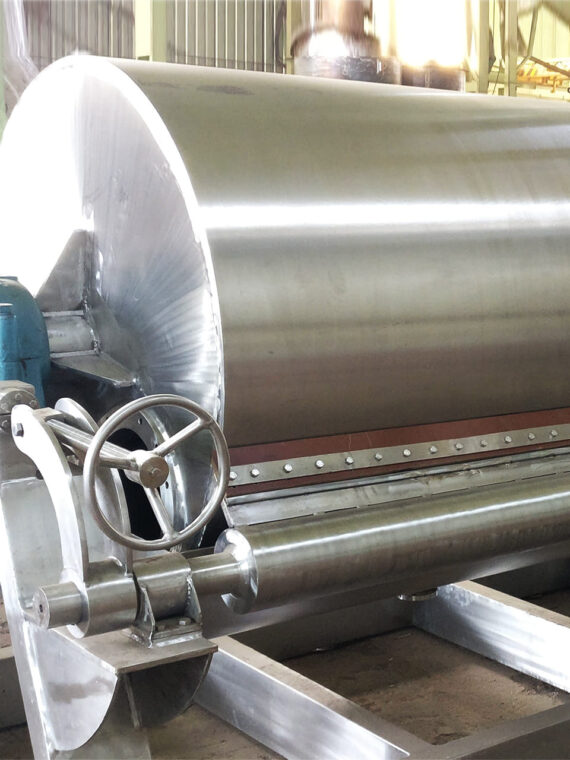
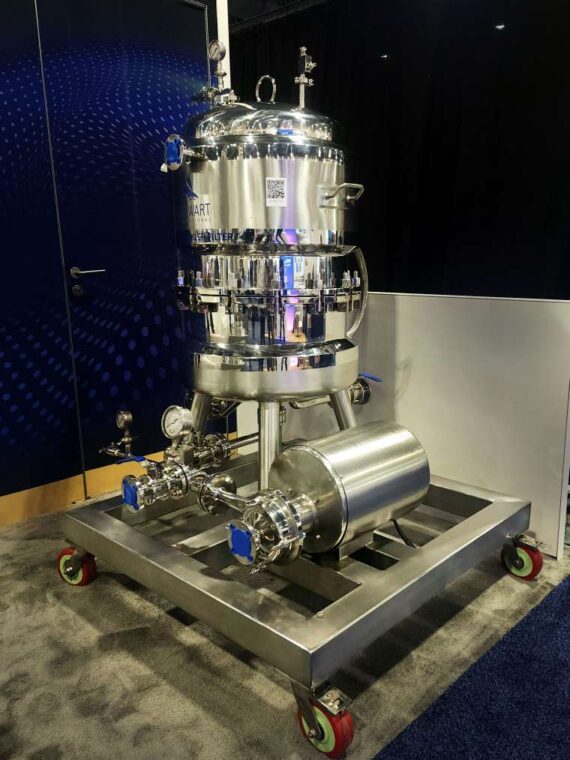
Reactors are the central elements of any chemical industry. They act as essential equipment for the transformation of raw materials into final products in industrial manufacturing. These versatile vessels come in various shapes and sizes, from small-scale laboratory reactors to massive industrial installations. They are used across a wide range of industries, from pharmaceuticals to petrochemicals, to catalyze chemical reactions and produce a multitude of products.
Chemical reactors are used across various industrial manufacturing processes, from making dyes and pigments to polymers, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, petrochemicals, etc. The following section provides an in-depth analysis of multiple applications of chemical reactors in industrial manufacturing, along with their associated advantages.
Chemical Reactors in Industrial Manufacturing
Chemical reactors form the heart of industrial manufacturing processes through their application in the following industries. It should be noted that the selection of reactors for each sector is based upon the reaction conditions, including thermodynamics and thermos-kinetics.
Pharmaceuticals
Chemical reactors are critical for the manufacturing of intermediate and APIs (active pharmaceutical ingredients) in the pharmaceutical industry. It incorporates specific manufacturing processes involving pressure and temperature regulation to yield high-quality medicinal products. Subsequently, different types of mixers, kilns, tubes, packed bed reactors, bioreactors, membrane and fluidized bed reactors, etc. Fluidized bed reactors are commonly employed for manufacturing powders and suspensions. Additionally, mixers are used to prepare syrups, ointments, and medicated creams. The ability to conduct reactions in a controlled environment ensures that the final products meet stringent regulatory standards for safety and efficacy.
Chemical Manufacturing
In chemical manufacturing, reactors occupy the central stage through the production of a wide range of chemicals and solvents. They are used in the making of plastics, polymers, fertilizers, nylon and multiple gases. For instance, the Haber-Bosch process uses a fixed-bed reactor with a catalyst under high temperature and pressure for ammonia synthesis. The ammonia thus produced is critical for the fertilizer and food industry. The efficiency of these reactors not only affects the yield of ammonia but also has implications for agricultural productivity worldwide.
Petrochemicals
In the petrochemical industry, reactors play a part in the conversion of crude oil into fuels and other chemical products. For instance, packed bed reactors are used in refineries for catalytic reactions like oxidation, hydrogenation, etc., while fluidized bed reactors are used for catalytic cracking, gasification, combustion and hydrocracking. Lastly, a fluidized catalytic cracker is widely used in petroleum refineries for the conversion of heavy petroleum fractions into lighter products. The efficiency of these reactors directly impacts yield and cost-effectiveness, making them vital for the profitability of oil refineries.
Food Processing
There are many procedures (such as emulsification and fermentation) in food processing that rely on reactors. For instance, microbes are cultivated in bioreactors to make yogurt or beer. The capacity to keep these biological processes in an ideal environment is critical for maintaining consistent and high-quality products.
Environmental Management
Environmental sustainability initiatives also benefit significantly from chemical reactors. Researchers in ecological science examine pollution and waste management using chemical reactors. They include processes involved in wastewater treatment for organic matter degradation or degradation of pollutants. Henceforth, chemical reactors can convert toxic waste into harmless by-products by chemical methods to reduce their environmental effect.
Biotechnology
Chemical reactors play a vital role in biotechnology by facilitating processes such as fermentation and cell culture. Bioreactors are purpose-built to provide ideal circumstances for the stimulation of microbial or cell proliferation for the synthesis of biopharmaceuticals, enzymes, and biofuels. They are also involved in the conversion of fossil fuels such as natural gas, oil and coal into energy.
Energy Production
Additionally, chemical reactors are crucial in the generation of sustainable energy sources like biofuels and hydrogen. Biofuels are derived from the conversion of biomass into fuel by reactors. The production of hydrogen involves the use of reactors to separate water into hydrogen and oxygen by a process known as electrolysis. Gasification and pyrolysis reactors transform organic residues into syngas or bio-oil, which may then undergo further refinement to produce sustainable fuels. This technology not only offers a substitute for fossil fuels but also aids in waste minimization by harnessing agricultural wastes and other organic waste products.
Read Also : Benefits of Utilizing Chemical Reactors in Industrial Operations
Importance of Chemical Reactors
Efficiency and Yield
Chemical reactors promote efficiency by adjusting reaction conditions to increase conversion rates and yields. For instance, continuous reactors provide continual manufacturing operations, which might result in better throughput than batch systems. This efficiency is crucial in satisfying market demands while keeping the operating expenses in check.
Safety
Chemical reactors are constructed with safety measures to minimize occupational hazards involved in chemical processing. These systems limit the chance of accidents or hazardous situations during manufacturing by managing reaction conditions and implementing fail-safes.
Economic Impact
Chemical reactors have multiple economic and sustainable benefits in industrial manufacturing. They increase the overall competitiveness of industrial operations in global markets by allowing for large-scale production with consistent quality at reduced prices.
Chemical reactors are essential in industrial production because they play a critical role in manufacturing high-value products efficiently and safely. Their relevance across industries emphasizes their position as the centre of industrial processes.
Read Also : Chemical Reactors – The Ultimate FAQ Guide