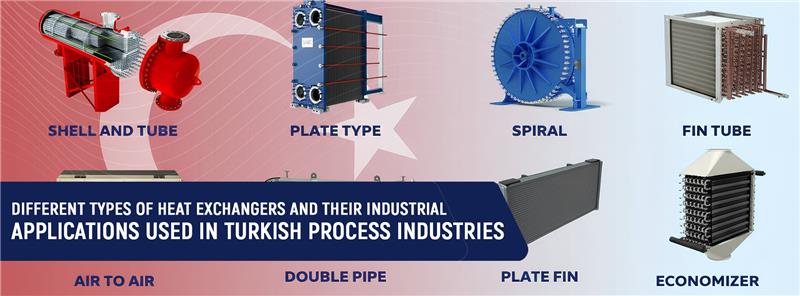
Heat exchangers are essential elements of the industrial process that allow transferring heat efficiently between the fluids without direct contact between the fluids. Heat exchangers have become critical factors in process industries that process the food and beverage sectors, chemicals, petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, oil and gas, power generation, textiles, mining, and wastewater treatment, which are rapidly growing in Turkey. With the Turkish industries taking more similar approaches to European efficiency and environmental requirements, the choice of the appropriate type of heat exchanger has become a strategic choice.
Significance of Heat exchangers in Turkish industrial plants
The industrial sector of Turkey is very diversified and export-oriented. Industrial facilities will be expected to be highly energy-efficient and have fewer emissions, as well as produce products of the same quality. Heat exchangers can assist in pursuing these objectives by maximizing thermal processes, minimizing energy usage, and facilitating sustainable production. The Turkish industries are using various heat exchanger designs depending on the conditions of the processes, like temperature, pressure, fluid type, and space availability.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
The most commonly used type in Turkish process industries is a shell and tube heat exchanger, as it is built with strength and is flexible. They are bundles of tubes that are enclosed in the form of a cylinder, with one fluid passing through the tubes and another around the tubes.
These heat exchangers are highly utilized at oil refineries, petrochemical plants, chemical manufacturing units, as well as power generation facilities in industrial zones like Kocaeli, İzmir, and Adana. They are most suitable in conditions that have high temperature, high pressure, and aggressive fluids like condensers, reboilers, and process heaters. They are easy to customize and durable, and hence are a favorite in heavy-duty industrial applications.
You can also read: Top 5 Benefits of Using Heat Exchangers in Industrial Applications
Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are also gaining popularity in Turkish industries, in which space efficiency and high thermal performance are very important. They are composed of thin corrugated metals that are called plates and provide a high heat transfer surface area within a small footprint.
Plate heat exchangers are also popular in the food and beverage processing sector, dairy plants, breweries, pharmaceutical processing, and HVAC in Turkey. Its uses are in the pasteurization of milk, in heating and cooling of juices, clean-in-place (CIP), and in temperature regulation during pharmaceutical procedures. They are suitable for the industries that are concerned with the quality and safety of the products, and are also highly efficient, easily cleaned, and meet the requirements of hygienic standards.
You may also like: Advantages And Mechanism Of The Corrugated Tube Heat Exchangers
Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
In some areas in Turkey, there is water scarcity, which has promoted the use of air-cooled heat exchangers. These systems do not need water; rather, ambient air is used as the cooling medium, and therefore, they are environmentally friendly and cost-effective in regions with limited water.
Applications of air-cooled heat exchangers include oil and gas processing facilities, petrochemical facilities, compressor stations, and power plants. They especially fit and are distant from the industries outdoors. These heat exchangers allow further lowering of operating costs and environmental impact by removing the cooling water requirement.
You can also read: Understanding Heat Transfer Efficiency in Modern Heat Exchangers
Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Finned tube heat exchangers are provided to amplify the capacity of heat transfer, particularly where one of the fluids is a gas. The fins enhance the amount of surface area, which enhances thermal performance.
Finned tube heat exchangers have become popular in waste heat recovery systems, flue gas cooling processes, dryers, and gas processing in the Turkish process industries. These exchangers are used by power plants and industries that consume a lot of energy, recovering waste heat, which leads to a reduction of energy and emissions.
Spiral Heat Exchangers
The spiral heat exchangers are particularly adapted to fluids that are viscous, foul, or based on slurry. Their spiral structure makes them highly turbulent and hence less foul as well as efficient at transferring heat.
Spiral heat exchangers are also widely used in sludge heating in wastewater treatment plants, pulp and paper industries, chemical processing, and oil sludge treatment in Turkey. Their small size and self-cleaning nature make them a perfect fit in demanding applications that other types of heat exchangers would not cope with.
You may also like: 2 Major Types Of Heat Exchangers Used In Various Industries For Various Application
Double Pipe Heat Exchangers
The heat exchanger is made of a single pipe inside another, known as a double pipe heat exchanger, and is applicable to rather small heat transfer tasks. They have a small capacity, yet they are appreciated due to their simplicity and affordability.
Turkish companies rely on the use of the double pipe heat exchanger in pilot plants, research and development, specialty chemical processing, and heating or cooling on a small scale. They are flexible and low-volume processes, and therefore, they are easily installed and maintained.
You may also read: Exporting Chemical Reactors and Heat Exchangers from India: A Complete Guide to EU Compliance
Plate and Shell Heat Exchangers
Plate and shell heat exchangers combine the compactness of a plate heat exchanger with the strength and pressure capability of a shell and tube design. This is a hybrid model that is on the rise in the Turkish process industries.
They are being applied in more chemical or petrochemical facilities, refrigeration systems, or in heat recovery units where high efficiency and a compact design are needed in harsh environments. Plate and shell exchangers provide a superior ratio between performance and life.
You may also like: Applications & Benefits of Decanter Centrifuges in Turkey
Conclusion
The types of heat exchangers used in Turkish process industries depend on the variety of requirements related to operation and environmental conditions. Though shell and tube heat exchangers are still a staple of heavy industries, plate, air-cooled, finned tube, spiral, double pipe, and plate and shell heat exchangers are used in particular industrial applications. The correct choice of the heat exchanger not only improves the energy efficiency but also provides the stable functioning of the process and contributes to the sustainability of the processes in the manufacturing industry.
The integration of effective and application-specific heat exchanger technologies will be crucial to the growth and competitiveness of the industry as Turkey maintains its status as a regional and global manufacturing center.
FAQs
1. What is the best type of heat exchanger?
There is no single best heat exchanger. The right choice depends on pressure, temperature, and application. Shell and tube heat exchangers are widely used in heavy industries for durability and high-pressure handling, while plate heat exchangers are preferred for compact design and high efficiency.
2. How many heat exchangers are there?
Heat exchangers are mainly divided into three categories: direct contact, indirect contact, and special-purpose types. Common industrial designs include shell and tube, plate, air-cooled, double pipe, and spiral heat exchangers, each selected based on process and performance needs.
3. What is a main heat exchanger?
A main heat exchanger is the primary unit responsible for transferring heat between two fluids within a system. It carries the major thermal load and ensures stable temperature control, improved energy efficiency, and smooth industrial operations.
4. What is the best material for heat transfer?
Materials with high thermal conductivity are best for heat transfer. Copper and aluminum provide excellent performance, but in industrial applications, stainless steel is commonly used because it offers durability, corrosion resistance, and reliable long-term operation.
5. What is the industrial strategy of Turkey?
Turkey’s industrial strategy focuses on strengthening domestic manufacturing, increasing exports, and investing in advanced technologies. The country supports sectors like machinery, automotive, defense, and energy while promoting innovation and reducing import dependency.
6. How is Turkey so advanced in technology?
Turkey has advanced through strong investment in research and development, defense systems, automotive manufacturing, and digital transformation. Government support, skilled engineers, and strategic trade connections have helped accelerate technological growth.