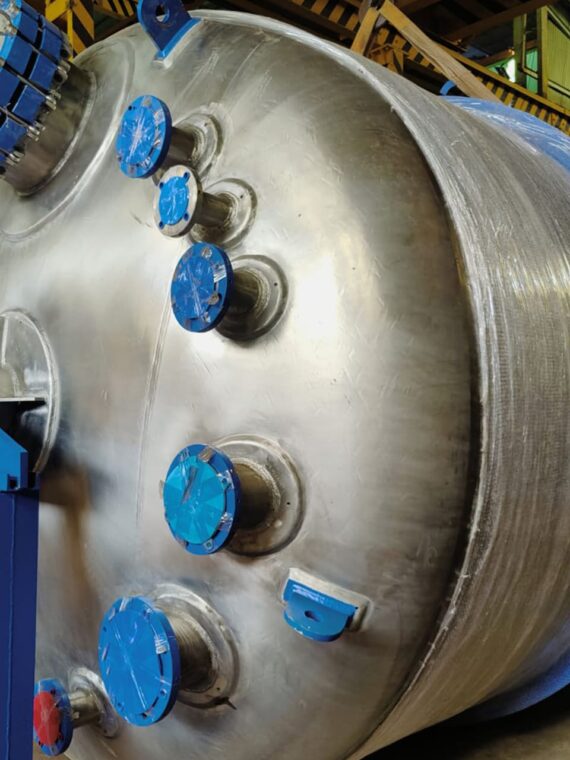
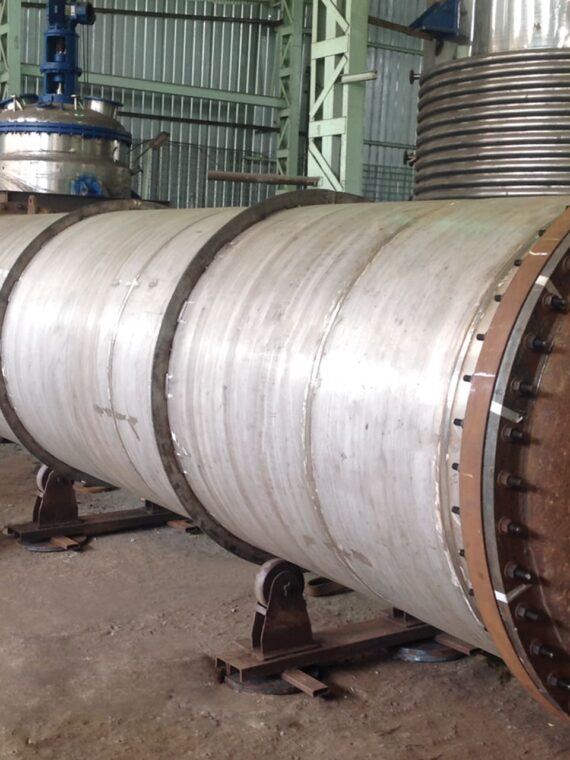
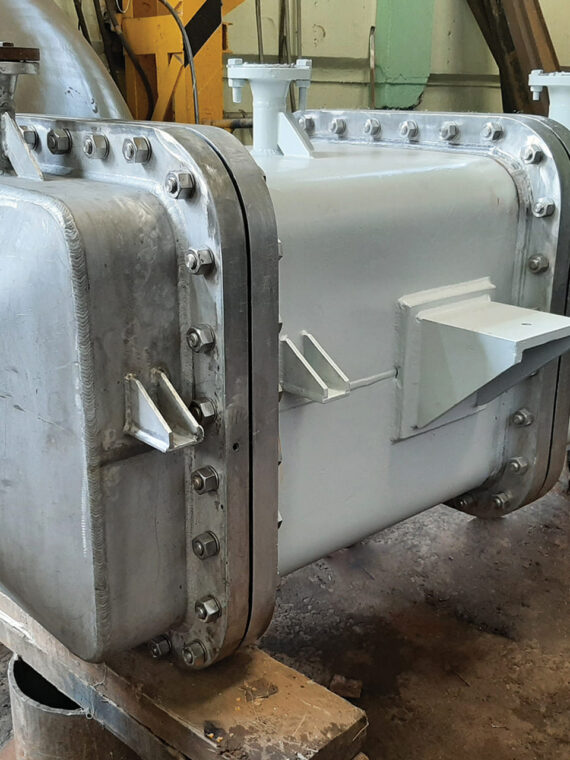
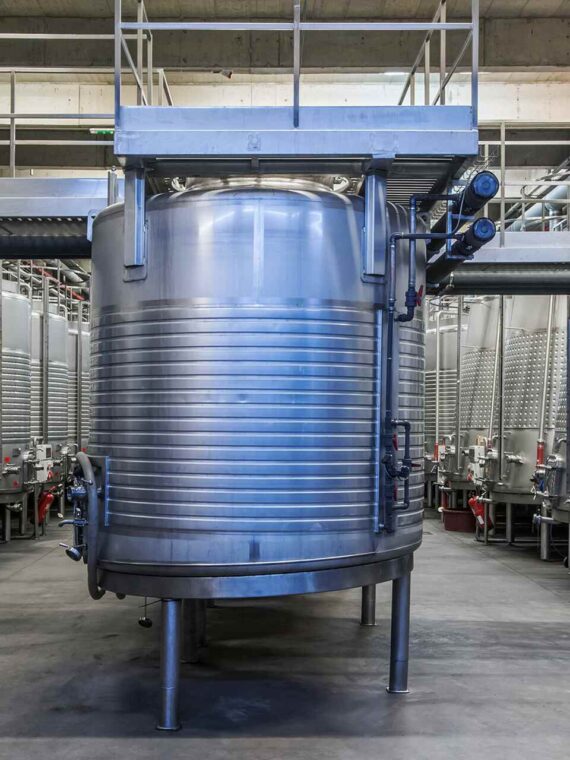
Maintainance of industrial equipment like heat exchanger involves lots of mechanical cleaning constraints requiring them to simple to clean. Stalwart International provides its expertise in modified heat exchangers by developing cost-effective and reliable products. Each of their products obeys the present food processing standards that are in force.
Heat exchangers used in various industries for various applications
Shell and tube heat exchanger: These heat exchangers are manufactured and designed to meet various energy requirements with the heavy duty of more than 70 MW.
Benefits of shell and tube heat exchanger:
- The shell and tube heat exchanger manufacturers in India ensure to develop a customized product as per your requirement.
- They provide complex applications: rare materials, high pressures.
- The experienced manufacturers are recognized by integrators.
- They have the necessary international quality certifications.
- The manufacturers know well about multi-tubes and bi-tubes exchangers and Shell and Twist tubular heat exchangers.
The manufacturers offer tubular heat solutions according to various types of operating conditions. There are heat exchangers that are about 3 meters long, under pressure or vacuum about 400 bar, produced from various materials like titanium, copper alloys, stainless steel, etc.
Standard or specific range tube exchangers
- Straight tube or U-tubes in shell
- Shell and Twist, corrugated and Bare tubes. In such a case, it is possible to have a counterflow heat exchanger.
- Double or simple tubular plates
- Removable or fixed bundles
Exchanger reconditioning
- Wound Coils
- Finned tube sets
- Replacement of bundles as per to models or drawings
- On-site or in the workshop
Electric heaters
- Without or with controls
- For gas
- For liquid
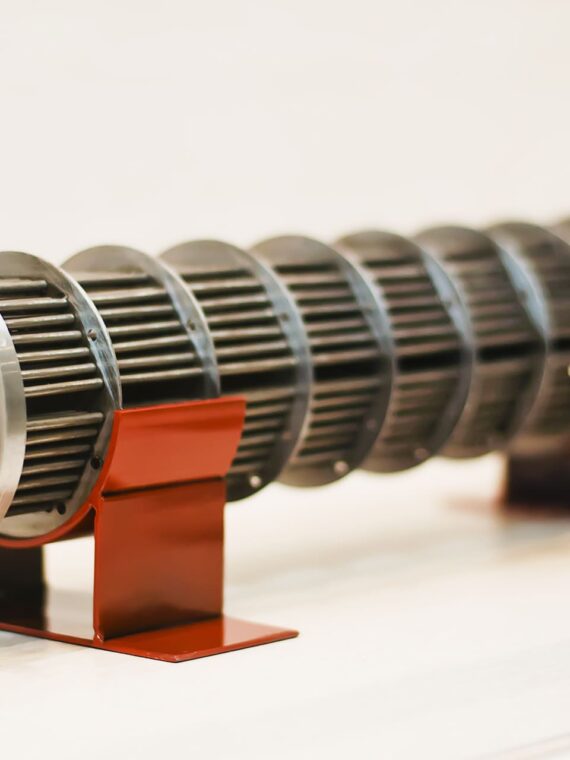
Corrugated tube heat exchanger:
Corrugations are developed by denting the tube beside the length in the helical pattern by utilizing a special purpose appliance developed for corrugation of pipe without the development of stresses or thinning of the wall in the tube.
The optimal height of the indentation and helical design of the corrugations results in a two-regime movement in the tube side liquid- eddies at periphery and spiral at core developing turbulence at a reduced velocity of fluid causing in greater heat transfer coefficient.
Must Read: Factors to Consider While Choosing a Heat Exchanger
Benefits of Corrugated Tube Heat Exchangers:
- Improved Condensation Efficiency: Encourages dropwise condensation rather than thin film formation, which enhances heat transfer.
- Enhanced Surface Renewal: The spiral design constantly renews the surface area for condensation, improving performance.
- Turbulent Flow: The helical indentations create internal turbulence, promoting better mixing and heat transfer.
- Uniform Temperature Distribution: Continuous flow ensures even temperature across the tube wall.
- Self-Cleaning Effect: High turbulence prevents solid particles from settling, leading to less fouling and longer operational time.
What’s New in the Market?
- Enhanced Corrugation Models: Especially for condensers, offering higher heat transfer efficiency.
- Compact and Economical Designs: Providing space and cost savings for industries.
- Advanced Material Manufacturing: Now available in materials like Super Duplex Steels, Tantalum, Titanium, and Hastelloy for more demanding environments.
You May Also Like: Top Heat Exchanger Maintenance Tips That Work
Conclusion
When selecting a heat exchanger, it’s crucial to consider ease of maintenance, performance efficiency, material compatibility, and compliance with industry standards. Stalwart International continues to stand out in the industry by delivering advanced, reliable, and efficient heat exchange solutions that meet the evolving needs of industrial applications.
Whether you require shell and tube or corrugated tube heat exchangers, you can count on Stalwart International—one of the trusted shell & tube Heat exchangers manufacturers—to deliver quality solutions that perform and endure.
FAQs
1. What are the two major types of heat exchangers used in industries?
The two major types of heat exchangers commonly used in various industries are Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers and Plate Heat Exchangers. Each serves different industrial applications based on heat transfer efficiency, fluid types, and space availability.
2. What is a shell and tube heat exchanger and where is it used?
A shell and tube heat exchanger consists of a series of tubes housed within a cylindrical shell. One fluid flows through the tubes, and another fluid flows over the tubes within the shell to transfer heat. It’s widely used in power plants, chemical processing, oil refineries, and HVAC systems.
3. How does a plate heat exchanger work?
A plate heat exchanger uses thin, corrugated metal plates stacked together, creating flow channels for two fluids. The fluids flow in alternate layers, allowing efficient heat transfer. It’s often used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and HVAC systems due to its compact size and high thermal performance.
4. Which industries commonly use heat exchangers?
Heat exchangers are essential in industries such as:
- Oil and Gas
- Power Generation
- Food and Beverage
- Chemical Processing
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning)
- Pharmaceuticals
- Marine and Automotive
5. What is the difference between shell and tube vs. plate heat exchangers?
The primary difference lies in their design and application. Shell and tube heat exchangers are more suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. They are larger, more robust, and are often used in heavy industries like oil refineries and power plants. Plate heat exchangers, on the other hand, are compact and more efficient in heat transfer due to their large surface area. They are easier to maintain and clean, making them ideal for industries where hygiene and space-saving are critical, like food and pharma.
6. What factors should be considered when choosing a heat exchanger?
Key considerations include:
- Type and temperature of fluids
- Pressure levels
- Space constraints
- Maintenance needs
- Heat transfer efficiency
- Cost and installation complexity
7. Are heat exchangers energy-efficient?
Yes, heat exchangers are highly energy-efficient systems designed to recover and reuse heat from industrial processes, reducing energy consumption and operational costs significantly.
8. Can heat exchangers be customized for specific applications?
Absolutely. Many manufacturers offer custom-designed heat exchangers tailored to industry-specific needs, fluid properties, temperature ranges, and space availability.
9. How often should industrial heat exchangers be maintained or cleaned?
Maintenance frequency depends on the application, but generally, industrial heat exchangers should be inspected and cleaned every 6 to 12 months to prevent fouling, scaling, and reduced efficiency.
10. What are common signs that a heat exchanger needs servicing?
Watch for these signs:
- Drop in heat transfer performance
- Increased pressure drop
- Unusual temperature readings
- Leaks or corrosion
- Fouling or scaling visible on inspection