Application and Advantages of Corrugated Tube Heat Exchanger
There are several industries (quite a large number of them) that employ processes which entail the transfer of heat between two fluids. Now, how exactly is the process of heat transfer conducted? We will unlock answers right here. Read on to explore!
How do heat exchangers work?
Two fluids at different temperatures are placed inside a heat exchanger and the heat is transferred from the hotter to the colder fluid until both the fluids reach the same temperature. Both these fluids are in constant contact with a tube wall which acts a conductive barrier. There are different types and styles of heat exchangers employed for this process. The industries select their exchangers in accordance with the purpose and condition of the site.
What is a corrugated tube heat exchanger? How does it work?
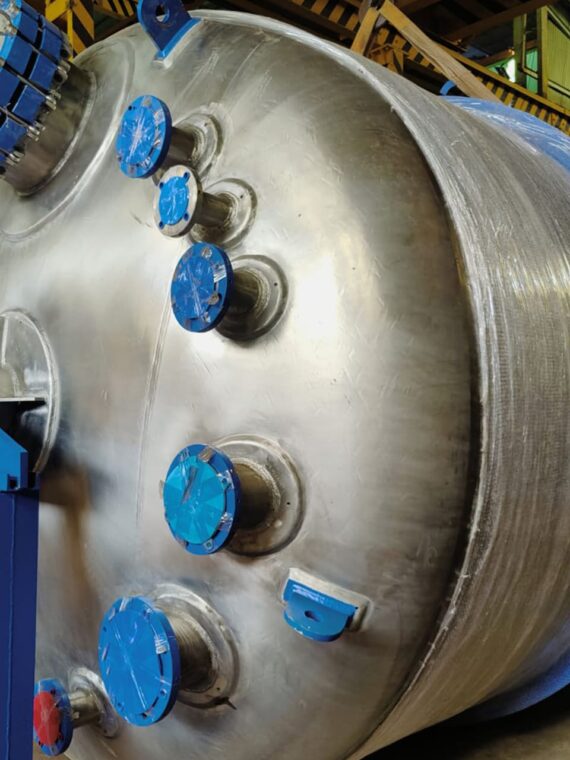
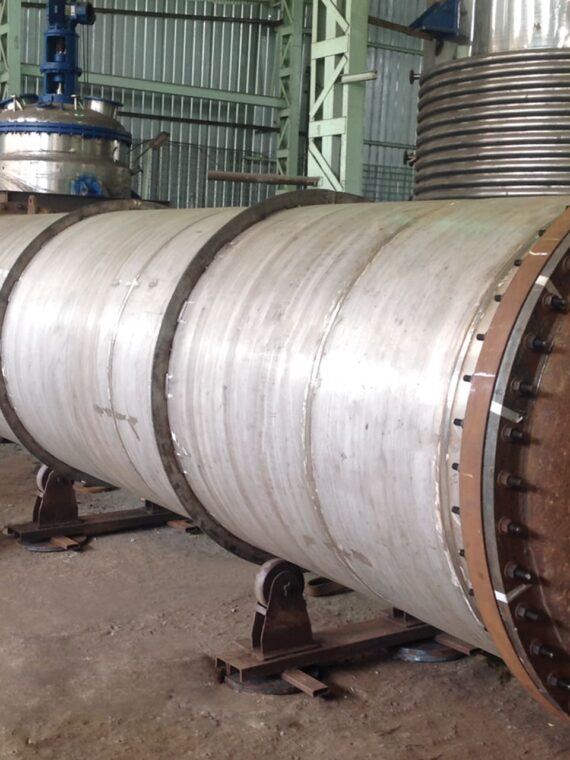
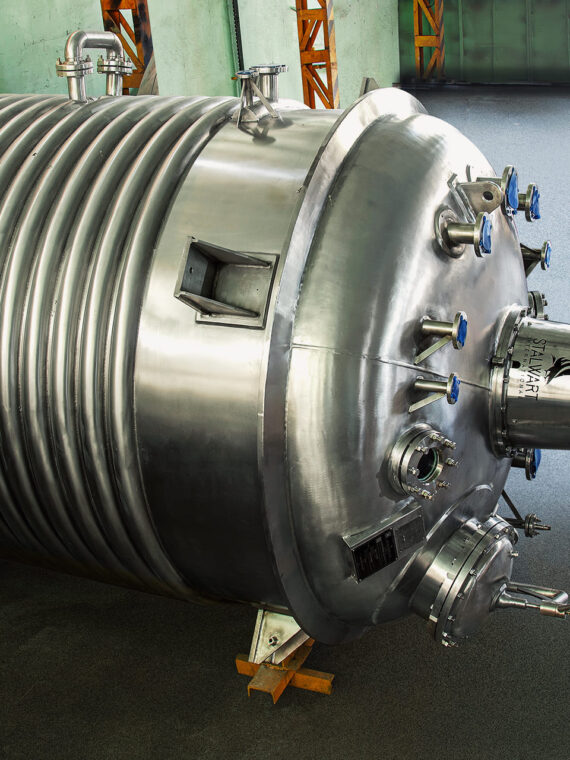
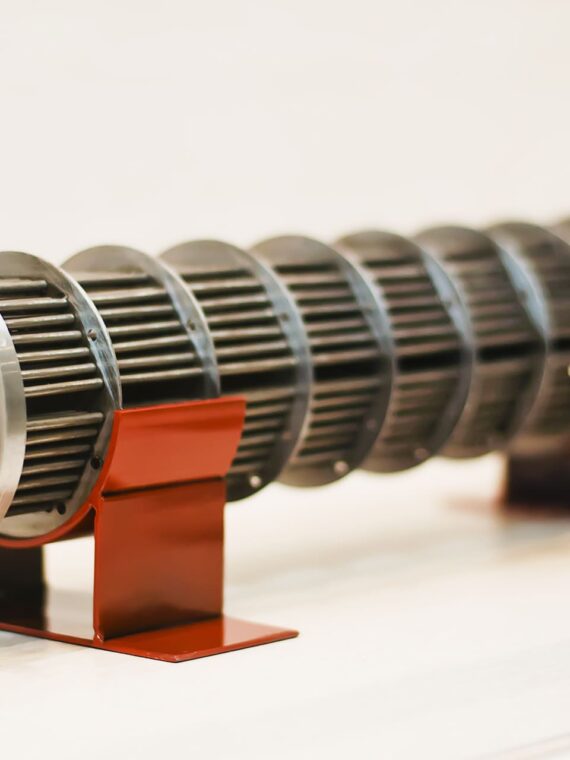
A corrugated tube heat exchanger remains a very popular type of heat exchanger used by industries today – and not without reasons. These heat exchangers perform by offering increased turbulence. This, in turn, renders higher heat transfer coefficient even at minimal Reynolds’s number. The corrugation of the tube shell, also known as programmed deformation is responsible for the higher turbulence in these exchangers. The corrugated tube shells offer spiral fluid flow as against the tubes with smooth shells.
The corrugated tube heat exchangers come with varying geometries. Hard corrugation paves the way for considerable improvement of the heat transfer coefficient, which again, makes up for the inevitable increase in pressure loss.
Features of the corrugated tube heat exchanger
- It has the smooth indented inner surface that allows for simple cleaning.
- Turbulence is developed at low fluid rates to improve heat transfer result in a higher heat transfer coefficient.
- Snarling on the tube shallow is minimized.
- It is available in a wide range of shapes and diameters.
Various corrugation geometries
Soft corrugation: Transitional between tube corrugation HARD and smooth tube design enhances heat transmission to a reduced extent, however with less pressure drop.
Hard corrugation: It permits to accomplish a high growth of heat transfer amount that rewards the inherent upsurge in pressure loss.
Must Read: Factors to Consider While Choosing the Right Heat Exchanger
Benefits of corrugated tube heat exchangers
Soft corrugation, on the other hand, allows for less improvement of heat transfer but the pressure drop is lower as well. Are you researching the types of heat exchangers at present? If yes, then you can rest assured that you’ll be coming across corrugated tube heat exchangers as something widely used in the industrial heat transfer processes. And why exactly is that? Needless to say, the heat exchangers are used widely – quite simply because of the fact that they offer a number of benefits. Here is a look at the string of advantages offered by them:
- They are associated with better heat transfer coefficient and thus are more compact
- They are very easy to install
- They offer high-induced turbulence thereby minimizing fouling – hence continue performing for a very long time to come
- Can be accessed in modular shapes so as to complement duty, as is required
- They can perform under high temperatures and pressure
- They can be employed for transferring process fluids with particulate matter
- Low-pressure drop
- Zero gasket failures compared to PHE
- Even the capital cost is lower compared to SHE/PHE
- There are various options that can be accessed while it is being installed – i.e. vertically, horizontally or in an inclined fashion
- Almost maintenance free
- No localized heating
- Suitable for products that are sensitive to heat
In order to make the most of the benefits of corrugated tubes, do make sure that you are procuring your corrugated from reputed industrial heat exchanger manufacturers.