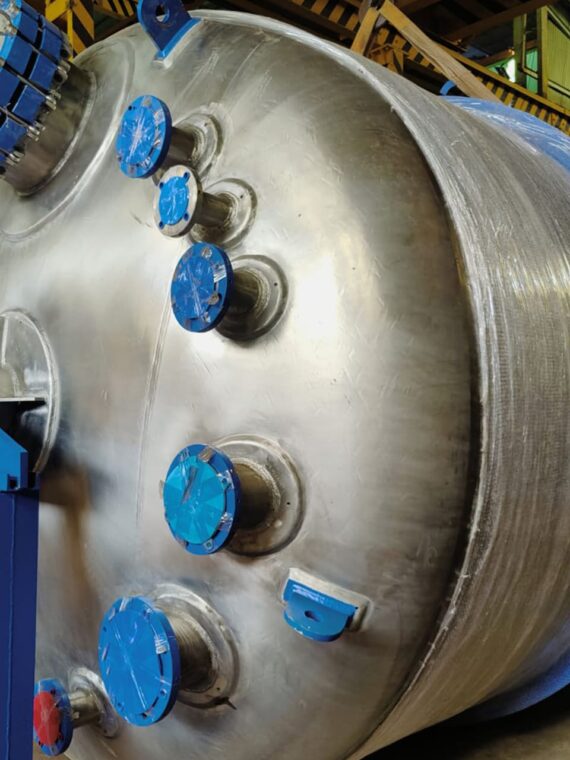
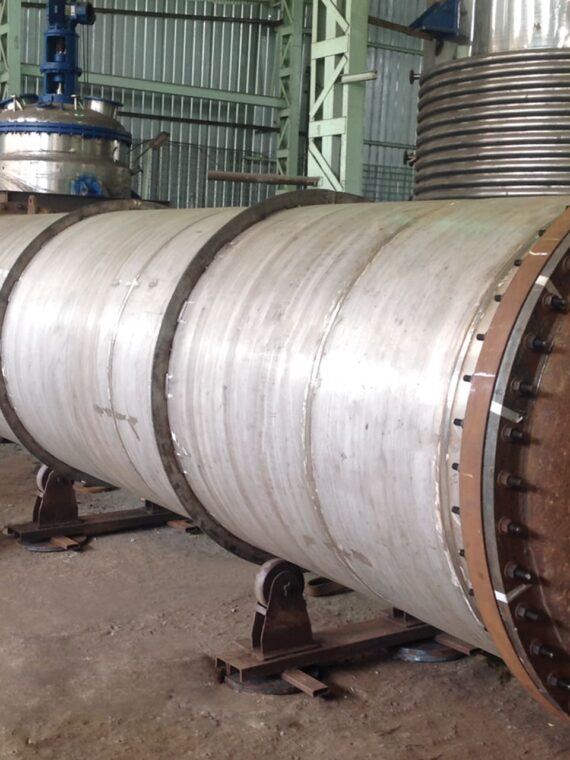
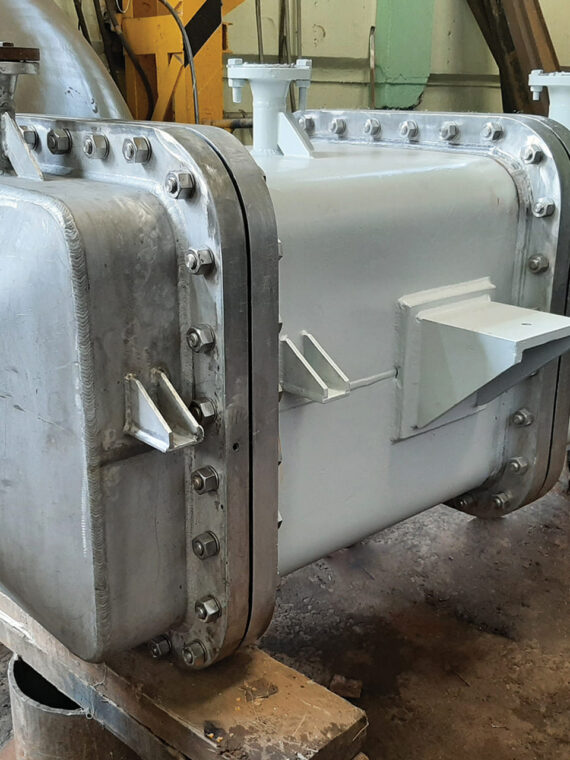
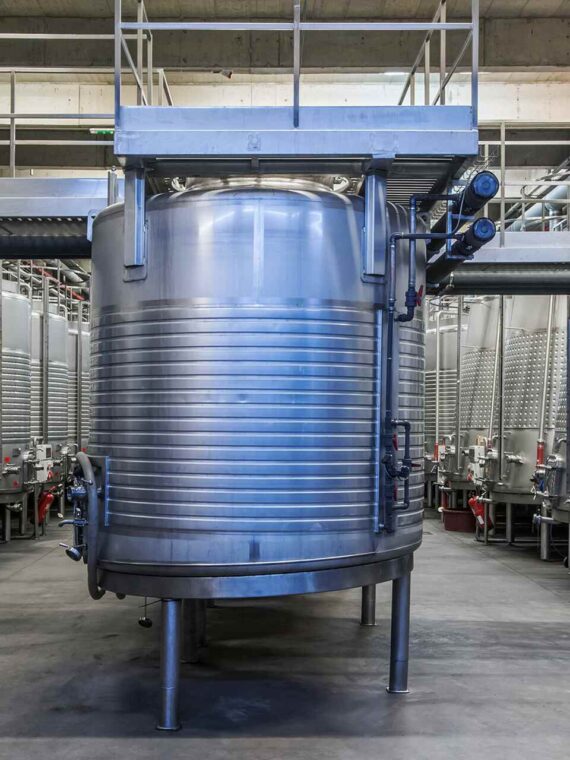
Heat exchangers have a vast majority of various industrial applications. They are optimal for the transfer of thermal energy between fluids. Such equipment has multiple advantages in terms of efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. The top five advantages of the usage of heat exchangers in industrial applications are given below:
Advantages of The Usage of Heat Exchangers in Industrial Applications
Energy Efficiency: Saving Dollars and Resources
Imagine slitting off your energy bills and becoming a better environmental steward. Heat exchangers help industries save energy by capturing and reusing wasted thermal energy. In any manufacturing process, the heat generated can return to the system, and less energy will be needed to complete the process. This lowers the operation cost and makes the production process much more sustainable. According to a study by the International Energy Agency (IEA), heat exchangers can save up to 40% of energy consumption in industrial processes. Hence, heat exchangers enable industries to save money and streamline manufacturing processes.
Weight and Space Efficiency
Heat exchangers are lightweight, allowing them to occupy confined spaces without compromising efficiency. Plate heat exchangers, in particular, can be up to 80% smaller than shell-and-tube heat exchangers, providing significant space savings in industrial facilities. Additionally, this space and weight efficiency also reduces challenges during the transport and installation of the equipment. In chemical plants or food processing facilities where every square foot counts, the compactness of machinery offers greater flexibility in layout design. Heat exchangers enable industries to maximize their operational footprint without being encumbered by big machinery.
Temperature Control
Temperature precision is critical in most industrial applications to ensure the safety and quality of the end products. Heat exchangers allow for optimal maintenance and regulation of fluid temperatures, ensuring product stability. For instance, in food and pharmaceuticals, a slight change in temperature may lead to spoilage. Heat exchangers fit remarkably well in this context owing to their ability to regulate temperatures. They also ensure the stability of intermediate and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in the pharmaceutical industry. The precise temperature and reaction regulation also helps streamline industries’ manufacturing operations. Thus, heat exchangers keep everything in the best thermal range to avoid inconsistency or irregularity in output quality.
Eco-Friendly Operations
With an increase in awareness about the environment, industries are doing their best to decrease their carbon footprint. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that heat exchangers can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 20% in specific industrial sectors. In the modern era, customers prefer companies known for their eco-friendly and sustainable practices. Heat exchangers are vital for industrial applications as they increase energy efficiency and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. They decrease reliance on fossil fuels by recovering waste heat from chemical reactions. For instance, the exhaust gases in power plants can preheat feedwater through an industrial heat exchanger. This would add to plant efficiency and cut down on emissions. Henceforth, it enables the companies to abide by environmental regulations and fulfill their corporate and social responsibility. Using heat exchangers is an optimal step towards a cleaner, greener future.
Versatility: One size fits all
Another exemplary virtue of heat exchangers is their unprecedented flexibility. It serves in the broadest possible diversity of industries: from power generation to oil refining, chemical processing to food manufacturing. Heat exchangers are used in over 80% of industrial processes, according to a survey by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). Different types of heat exchangers, shell-and-tube, plate, air-cooled, and double-pipe, are designed to accomplish various tasks depending on the operating conditions, the nature of the fluid, and operating conditions.
For example:
- Shell-and-tube heat exchangers are well-suited for high-pressure processes like oil refining.
- Plate heat exchangers are employed in food processes owing to their efficiency and easy cleanup
- Air-cooled heat exchangers commonly find their use in power plants where water resources are limited.\
The features of heat exchangers enable them to handle various fluids under variable conditions, thus making them suitable for a wide range of applications. This versatility ensures heat exchangers work with all types of materials, from molten metals to boiling liquids, and processes with high temperature and pressure requirements.
You May Also Like: Application Of Heat Exchangers Used In Food Processing And Nutraceuticals Industry
Conclusion
Heat exchangers are a part and parcel of an industrial process with many advantages, including saving energy, providing accurate temperature control, eco-friendliness, and space efficiency. As industries strive for better efficiency and greater environmental friendliness in an increasingly competitive landscape, these devices will be essential in shaping a sustainable future. Advanced heat exchanger technology has paved the way for sustainable industrial practice regarding sustainability, performance, and cost savings.
If you’re thinking about adding or upgrading a heat exchanger in your industrial application, so you can Contact us for more details or assistance.
FAQs
1. What are the main benefits of using heat exchangers in industrial applications?
Heat exchangers improve energy efficiency, reduce operational costs, enhance process control, minimize environmental impact, and extend equipment lifespan.
2. How do heat exchangers improve energy efficiency in industries?
They recover and reuse waste heat from one process stream to preheat another, reducing overall energy consumption and fuel costs.
3. Which industries benefit most from heat exchangers?
Industries like chemical processing, oil and gas, power generation, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals rely heavily on heat exchangers for heating, cooling, and thermal regulation.
4. What are the common types of heat exchangers used in industrial applications?
The most common types include shell and tube, plate, air-cooled, double pipe, and spiral heat exchangers.
5. What factors determine the useful life of a heat exchanger?
Material quality, maintenance frequency, operating temperature, fluid properties, and corrosion resistance determine the lifespan, typically ranging from 10 to 20 years.