The FMCG business in the Netherlands is among the most technologically advanced food-producing ecosystems in Europe. Dutch FMCG suppliers are highly productive, characterized by export expansion and rigorous regulatory compliance, resulting in rapid, high-quality, compliance-level food processing machines at scale.
It is dairy and beverages, sauces, snacks, frozen foods, or plant replacements; regardless, the basis of this success is hygienic, efficient, and consistent process manufacturing equipment.
Why the Netherlands Leads in FMCG Manufacturing
Multinational companies such as Unilever, FrieslandCampina, and Heineken have sophisticated plants in the country. Dutch FMCG manufacturers support the European and global markets through efficient logistics provided by the Port of Rotterdam.
Nevertheless, global leadership is not only maintained by location but also by the best-in-class food processing equipment deployed at all levels of manufacturing.
Key Food Processing Equipment Used in FMCG Manufacturing
1. Raw Material Handling Equipment
The production of FMCGs is efficient since the raw materials are managed.
Examples of acquired equipment include:
- Bulk bag unloaders
- Screw conveyors
- Conveying systems Pneumatic conveying systems.
- Silervent raw material tank storage.
Such systems make sure of controlled movement of materials, minimized contamination and continuous production vital to high volume FMCG systems.
2. Macking, Blending, and Processing Apparatus
The consistency, feel, and taste of the products are determined in this stage. Used machinery typical of a Dutch food factory:
- Paddle mixers (ribbon mixers, paddle mixers)
- High-shear mixers
- Homogenizers and emulsifiers.
- Batch reactors
- Continuous reactors
The necessity to use homogenizers and emulsifiers to regulate the quality of the particles and provide the formulations that remain stable in the situations of making sauces, dairy products, beverages, and plant-based foods contribute to the stable quality of each batch of the products made.
3. Thermal Processing Machinery
Thermal control is a necessity in food safety, shelf life and compliance. Key equipment includes:
- Pasteurizers
- Sterilizers
- UHT (Ultra-High Temperature) Systems.
- Plate-and-shell and shell-and-tube heat exchangers.
- Cooking kettles
Dutch FMCG manufacturers use heat exchangers and pasteurization systems that are highly regulated to eliminate pathogens without compromising nutritional value and taste, which are particularly important in dairy, infant food, and ready-to-eat products.
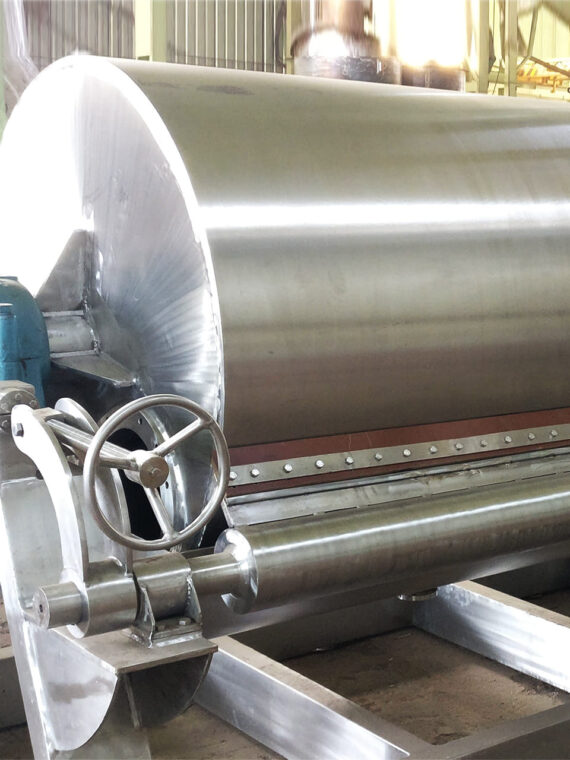
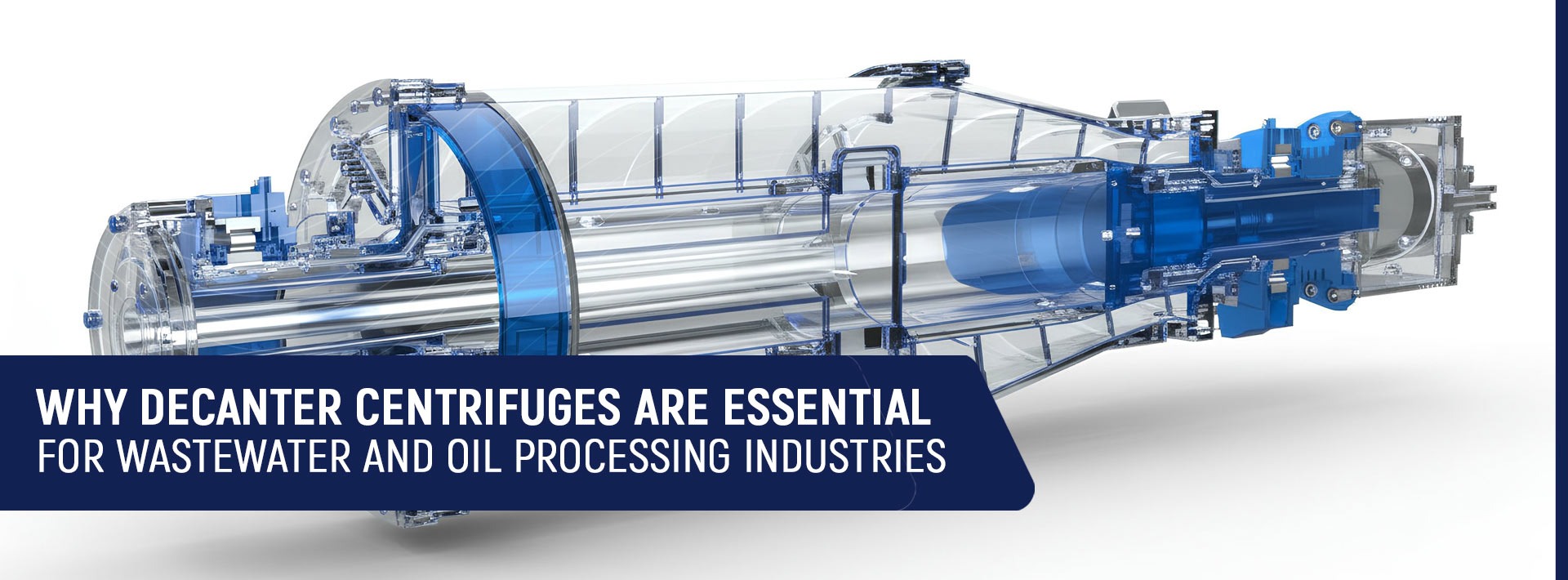
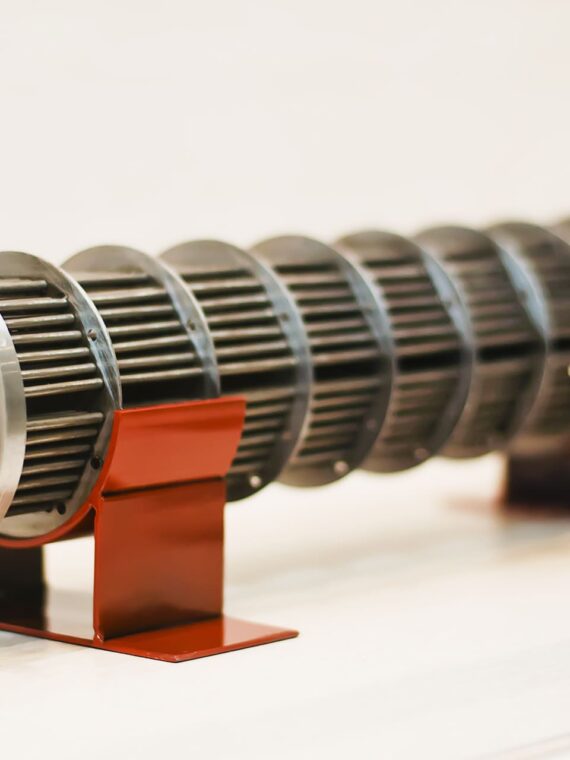
4. Separators, Filtration and Refiners
To reach purity and gain homogeneity of products, manufacturers use:
- Centrifuges
- Decanters
- Filters and strainers
- Clarifiers
The impurities are removed, the moisture content is regulated, and the products have a more desirable appearance, which is required for beverages, oils, dairy, and liquid FMCG products.
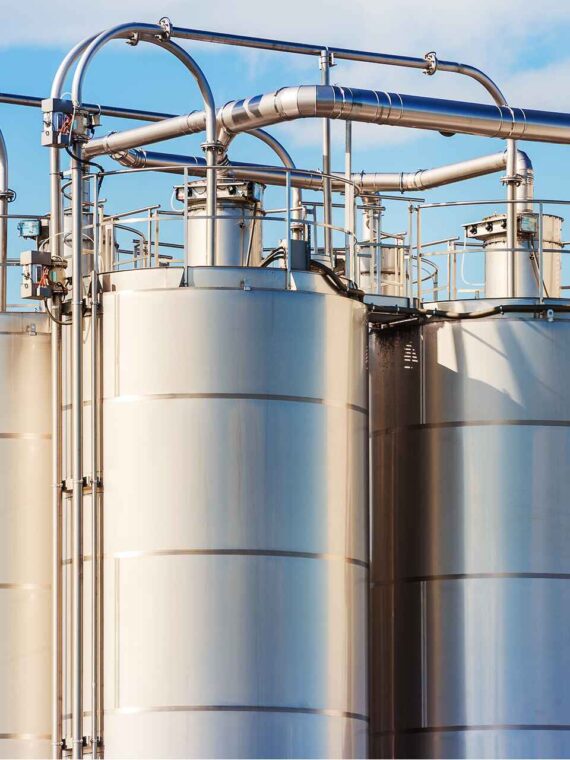
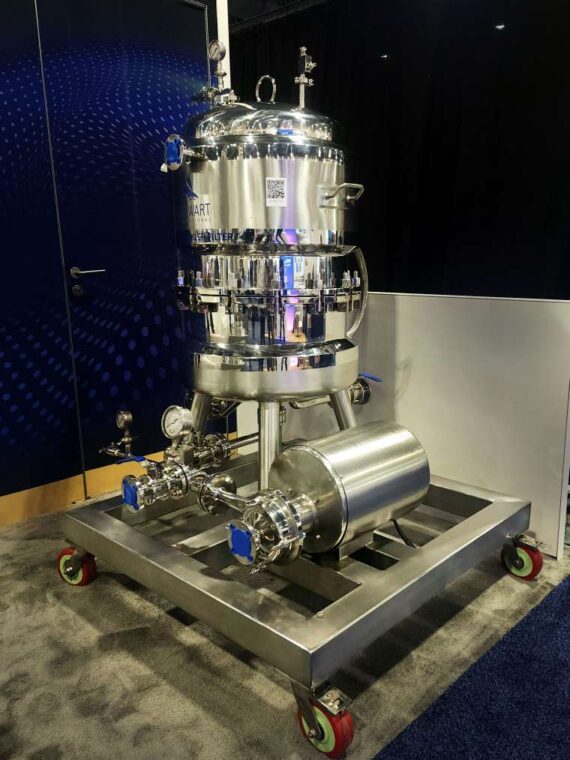
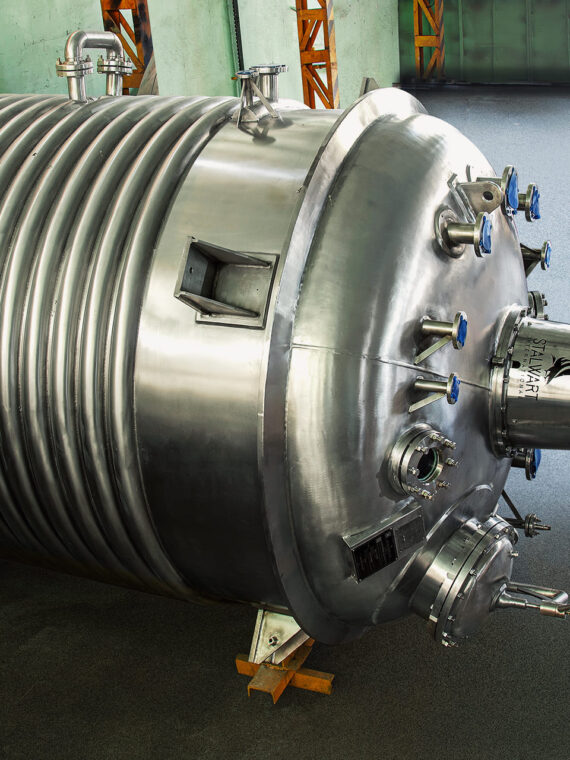
5. The Hygienic Storage and Transfer Systems
Storing and transferring of products between process stages is achieved by:
- Storage tanks: stainless steel.
- Pressure vessels
- Agitated tanks
- Food-grade centrifugal, lobe, and diaphragm pumps.
None of the equipment violates the principles of hygienic design: the interiors of all equipment are smooth and sanitary, and the valves are certified to FDA/EU standards, ensuring food safety and allowing them to be washed easily.
6. Cleaning, Hygiene Machines (CIP Systems)
EU food standards are dogmatic in hygiene.
Standard systems include:
- CIP (Clean-In-Place) skids
- Automated wash cycles
- Chemical dosing systems
CIP systems reduce manual cleaning, improve business availability, and ensure uniform cleaning, which is the most crucial aspect within the HACCP, BRCGS, and ISO guidelines in the Netherlands.
7. Packaging & End of Line Equipment
Speed and display are essential in FMCG.
The important packaging equipment is:
- Form-fill-seal machines
- Bottle filling/ capping machines.
- Cartoning machines
- Labeling machines
- Robotic depalletizers as well as palletizers.
High-speed automated packaging lines help Dutch manufacturers support multiple SKUs, own-label, and export package designs.
Impact of Equipment on Speed, Quality, and Compliance
Speed
Automatic mixers, continuous reaction operations, and robotic package lines make it possible for high volumes of production to occur 24/7, allowing it to satisfy market demands.
Quality
This is because accurate machinery such as homogenizers, pasteurizers, and controlled reactors enables a consistent product quality in terms of texture, flavor, and safety.
Compliance
Manufacturers of food have the confidence to comply with the strict EU food safety regulations through hygienic design, CIP systems, traceability-enabled controls, and digital batch records.
You May Also Like: Fmcg Equipment Sales In The Netherlands
The Strategic Advantage of Advanced Equipment
Food processing equipment is an investment to secure strategic growth rather than a cost center in the Netherlands. The FMCG manufacturers, through the right mix of reactors, heat exchangers, storage tanks, and automated packaging systems, are in a position to:
- Mass production is making it work.
- Maintain premium quality
- Breeze through international audits.
- Promote green production objectives.
Conclusion
The FMCG market in the Netherlands is advanced, with the latest food processing machinery, including raw material processing equipment, reactors, pasteurizers, CIP systems, and packaging line robots. The technologies directly affect speed, quality, and compliance, enabling Dutch manufacturers to compete internationally.
As Chinese companies step up consumer demands and requirements, demand stricter regulations, and invest in high-performance food processing equipment, hygienic standards, and automation, these will remain the hallmarks of success in the Dutch FMCG industry.
FAQs
What are the factors affecting the FMCG sector?
The FMCG sector is influenced by consumer demand, pricing sensitivity, raw material costs, supply chain efficiency, distribution reach, branding, and regulatory policies. Economic conditions, urbanization, and changing consumer preferences—especially toward health and convenience—also play a major role.
What is the biggest challenge in FMCG supply chain management for seasonal products?
The biggest challenge is demand forecasting. Seasonal products face unpredictable demand spikes, short selling windows, and high risk of overstock or stockouts. Poor forecasting leads to wastage, increased storage costs, and lost sales opportunities.
How to increase distribution in FMCG?
FMCG distribution can be increased by expanding distributor networks, strengthening last-mile delivery, using data-driven route planning, and partnering with local retailers. Digital ordering systems and strong logistics support are critical for faster and wider market penetration.
What is the role of packaging in maintaining food quality?
Packaging protects food from moisture, air, light, and contamination. It helps extend shelf life, preserves freshness, prevents spoilage, and ensures product safety during storage and transportation, especially in high-volume FMCG supply chains.
What are the risks of food packaging?
Food packaging risks include chemical migration from packaging materials, environmental pollution, improper sealing, and contamination. Poor-quality packaging can reduce shelf life, affect food safety, and damage brand credibility if regulations are not followed.